box plot directly comparing the distributions of each subject In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment. En esta edición de "5 Original Albums In 1 Box", se incluyeron un buen puñado de Bonus Tracks (16 marcados al reverso en el track list, más 5 o 6 canciones no incluidas originalmente en uno de los discos, aunque no estén marcadas como tal).
0 · symmetrical box plot
1 · symmetrical box distribution
2 · how to find box distribution
3 · box vs whisker plot
4 · box plots explained
5 · box plot calculation
6 · box plot anatomy
7 · box and whisker plot example
Choosing the right combination of metal roof and siding colors can elevate the aesthetic appeal of your home to new heights. In this section, we’ll explore twenty stunning color pairings that promise to harmonize perfectly with your home’s architecture and enhance its visual charm. 1. Classic Charcoal Roof with White Siding.The siding of your home is the largest surface area of your home’s exterior, and its color can greatly affect the look of your metal roof. A metal roof and siding color combination that doesn’t complement each other may result in a jarring and unbalanced appearance. On the other hand, a well-thought-out . See more
When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare .
Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the .
symmetrical box plot
symmetrical box distribution
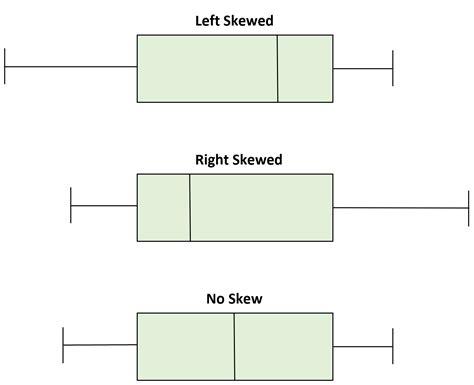
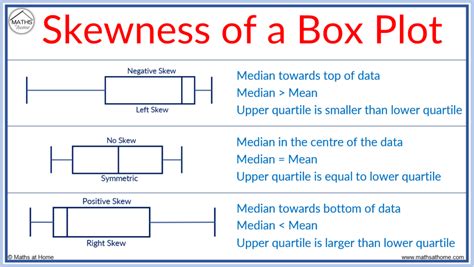
In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize . In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.Box plots are particularly useful for data analysis when comparing two or more data sets; it is easy to make visual comparisons of average (median) and spread (range and interquartile range). When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median .
Box plots offer a quick and informative way to: Visualize spread: Show how data varies within a set. Identify key values: See the median, quartiles, and potential outliers. Compare datasets: Easily compare distributions side-by-side. How .In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment. A box plot is constructed from five values: the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value. We use these values to compare how close other data values are to them. To construct a . When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles. From this, the spread and skew of the data can also be seen.In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable.
In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.Box plots are particularly useful for data analysis when comparing two or more data sets; it is easy to make visual comparisons of average (median) and spread (range and interquartile range). When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?
Box plots offer a quick and informative way to: Visualize spread: Show how data varies within a set. Identify key values: See the median, quartiles, and potential outliers. Compare datasets: Easily compare distributions side-by-side. How can this resource help? This resource provides a clear explanation and examples: Explanation: Defines box .In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment. A box plot is constructed from five values: the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value. We use these values to compare how close other data values are to them. To construct a box plot, use a horizontal or vertical number line and a rectangular box. When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?
how to find box distribution
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles. From this, the spread and skew of the data can also be seen.In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable. In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
Box plots are particularly useful for data analysis when comparing two or more data sets; it is easy to make visual comparisons of average (median) and spread (range and interquartile range). When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?
Box plots offer a quick and informative way to: Visualize spread: Show how data varies within a set. Identify key values: See the median, quartiles, and potential outliers. Compare datasets: Easily compare distributions side-by-side. How can this resource help? This resource provides a clear explanation and examples: Explanation: Defines box .
In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
box vs whisker plot

box plots explained
box plot calculation
box plot anatomy
$65.00
box plot directly comparing the distributions of each subject|symmetrical box plot