electric field of a point charge rectangular box To find the electric field at a point due to a point charge, proceed as follows: Divide the magnitude of the charge by the square of the distance of the charge from the point. Multiply the value from step 1 with Coulomb's . Available in a variety of colors and finishes, this premium-quality nontoxic paint is .
0 · equation for electric field charge
1 · electrical field of charge formula
2 · electrical field of charge calculation
3 · electric field due to positive charge
4 · electric field due to one charge
5 · electric field by point charge
6 · charged particle electrical field
7 · calculate electric field by point charge
TLDR: Can I use existing outlet boxes as junction boxes for short (12") runs to a new box and outlet? EDIT: The answer is yes, but only if the junction boxes are accessible. We are in the .
In Figure-01 we have a finite rectangular plate with uniform surface charge density σ arranged symmetrically with respect to the x − axis and y − axis separately. We want to find the electric field intensity vector E at the field point . The electric field at point \(P\) can be found by applying the superposition principle to symmetrically placed charge elements and integrating. Solution Before we jump into it, what do we expect the field to “look like” from . Analyze the vector component diagram to get the magnitude and direction of the resultant. A charged particle (a.k.a. a point charge, a.k.a. a source charge) causes an electric field to exist in the region of space around itself. . To find the electric field at a point due to a point charge, proceed as follows: Divide the magnitude of the charge by the square of the distance of the charge from the point. Multiply the value from step 1 with Coulomb's .
In this problem, we are going to show step by step how to calculate the electric field at any point due to multiple point charges. First we will draw the electric field due to each one of the .The direction of the electric field at point P is obtained from the symmetry of the charge distribution and the type of charge in the distribution. Therefore, Gauss’s law can be used to determine \(\vec{E}\).Electric Field of a Point Charge. Our first example is to find the electric field of a point charge +Q. To start this problem, we have to know the direction of the field. The electric field lines from a point charge are pointed radially outward from .At each corner of the box sits a point charge. (a) What is the Electric Field at the centre of the box ?? (b) What is the Electric Potential at the centre of the box ?? (c) Now you remove .
You can see how to calculate step by step the electrostatic potential due to the point charges q 1 and q 2 in this page. First, we will represent the charges and point P in a cartesian coordinate system. The unit vectors we are going to use . In Figure-01 we have a finite rectangular plate with uniform surface charge density σ arranged symmetrically with respect to the x − axis and y − axis separately. We want to find the electric field intensity vector E at the field point P = (0, 0, h) on the z − axis. The electric field at point \(P\) can be found by applying the superposition principle to symmetrically placed charge elements and integrating. Solution Before we jump into it, what do we expect the field to “look like” from far away?
Analyze the vector component diagram to get the magnitude and direction of the resultant. A charged particle (a.k.a. a point charge, a.k.a. a source charge) causes an electric field to exist in the region of space around itself. This is Coulomb’s Law for the Electric Field in conceptual form. To find the electric field at a point due to a point charge, proceed as follows: Divide the magnitude of the charge by the square of the distance of the charge from the point. Multiply the value from step 1 with Coulomb's constant, i.e., 8.9876 × 10⁹ N To calculate the electric field flux we introduce a suitable Gaussian surface (a rectangular box in this case). The top of the box is within the capacitor plate and does not have any electric flux cutting it.
In this problem, we are going to show step by step how to calculate the electric field at any point due to multiple point charges. First we will draw the electric field due to each one of the charges at the center of the rectangle.The direction of the electric field at point P is obtained from the symmetry of the charge distribution and the type of charge in the distribution. Therefore, Gauss’s law can be used to determine \(\vec{E}\).Electric Field of a Point Charge. Our first example is to find the electric field of a point charge +Q. To start this problem, we have to know the direction of the field. The electric field lines from a point charge are pointed radially outward from the charge (Figure fig:eField). Mathematically we can write that the field direction is . We .At each corner of the box sits a point charge. (a) What is the Electric Field at the centre of the box ?? (b) What is the Electric Potential at the centre of the box ?? (c) Now you remove one of the charges - what is the magnitude of the Electric Field at the centre of the box ??
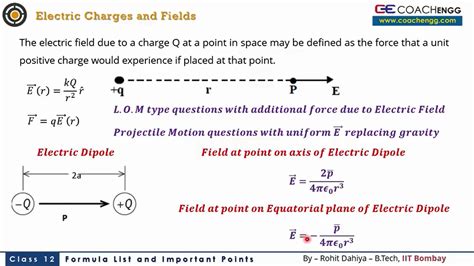
equation for electric field charge
You can see how to calculate step by step the electrostatic potential due to the point charges q 1 and q 2 in this page. First, we will represent the charges and point P in a cartesian coordinate system. The unit vectors we are going to use to calculate the electric fields E 1 and E 2 are represented in red in the figure. In Figure-01 we have a finite rectangular plate with uniform surface charge density σ arranged symmetrically with respect to the x − axis and y − axis separately. We want to find the electric field intensity vector E at the field point P = (0, 0, h) on the z − axis. The electric field at point \(P\) can be found by applying the superposition principle to symmetrically placed charge elements and integrating. Solution Before we jump into it, what do we expect the field to “look like” from far away? Analyze the vector component diagram to get the magnitude and direction of the resultant. A charged particle (a.k.a. a point charge, a.k.a. a source charge) causes an electric field to exist in the region of space around itself. This is Coulomb’s Law for the Electric Field in conceptual form.
To find the electric field at a point due to a point charge, proceed as follows: Divide the magnitude of the charge by the square of the distance of the charge from the point. Multiply the value from step 1 with Coulomb's constant, i.e., 8.9876 × 10⁹ N
To calculate the electric field flux we introduce a suitable Gaussian surface (a rectangular box in this case). The top of the box is within the capacitor plate and does not have any electric flux cutting it.
In this problem, we are going to show step by step how to calculate the electric field at any point due to multiple point charges. First we will draw the electric field due to each one of the charges at the center of the rectangle.The direction of the electric field at point P is obtained from the symmetry of the charge distribution and the type of charge in the distribution. Therefore, Gauss’s law can be used to determine \(\vec{E}\).
Electric Field of a Point Charge. Our first example is to find the electric field of a point charge +Q. To start this problem, we have to know the direction of the field. The electric field lines from a point charge are pointed radially outward from the charge (Figure fig:eField). Mathematically we can write that the field direction is . We .At each corner of the box sits a point charge. (a) What is the Electric Field at the centre of the box ?? (b) What is the Electric Potential at the centre of the box ?? (c) Now you remove one of the charges - what is the magnitude of the Electric Field at the centre of the box ??


galvanized steel outlet box

electrical field of charge formula
Today crafters still turn to TULIP for inspiration through their favorite techniques while discovering the ease and beauty of exciting new dimensional painting with TULIP paints. Tulip ColorShot Instant Fabric Spray Color 3oz. Black. Try again! GRPerks!
electric field of a point charge rectangular box|electric field due to positive charge